Unlocking the World of Cannabis Terpenes: Gain Insight into Plant Production and the Top 10 Terpenes
Exploring the world of cannabis unveils a rich tapestry of scents, flavors, and effects intricately woven by nature’s aromatic compounds known as terpenes. These organic molecules not only define the olfactory experience but also contribute significantly to the nuanced effects of various cannabis strains. In this comprehensive exploration, we embark on a journey to understand the intricate mechanisms behind terpene production in cannabis plants and unveil the top 10 most abundant terpenes, each with its distinct characteristics and potential therapeutic benefits.
Terpenes represent significant constituents within marijuana resin, paralleling their prevalence in the aromatic essential oils found abundantly across various plant species. These oils, comprising the essence of most flowers, herbs, and spices, bear the distinctive hallmark of terpenes. A mere pinch of a cannabis bud releases these fragrant molecules, a sensory cue familiar to connoisseurs. Whether encountering the citrus zest of Grapefruit, the earthy allure of Silver Haze, or the fruity notes of Blueberry, each aroma hints at the ensuing psychoactive experience. Notably, terpene production escalates as the plant prioritizes reproduction, amplifying the bouquet as flowering advances. From the subtle whispers preceding blossoming to the robust fragrance enveloping mature buds, terpenes serve as heralds of cannabis’s developmental journey.
As Cannabis Progresses Through Its Reproductive Stages, It Initiates The Synthesis Of Terpenes Within The Glands Enveloping Its Flowers.
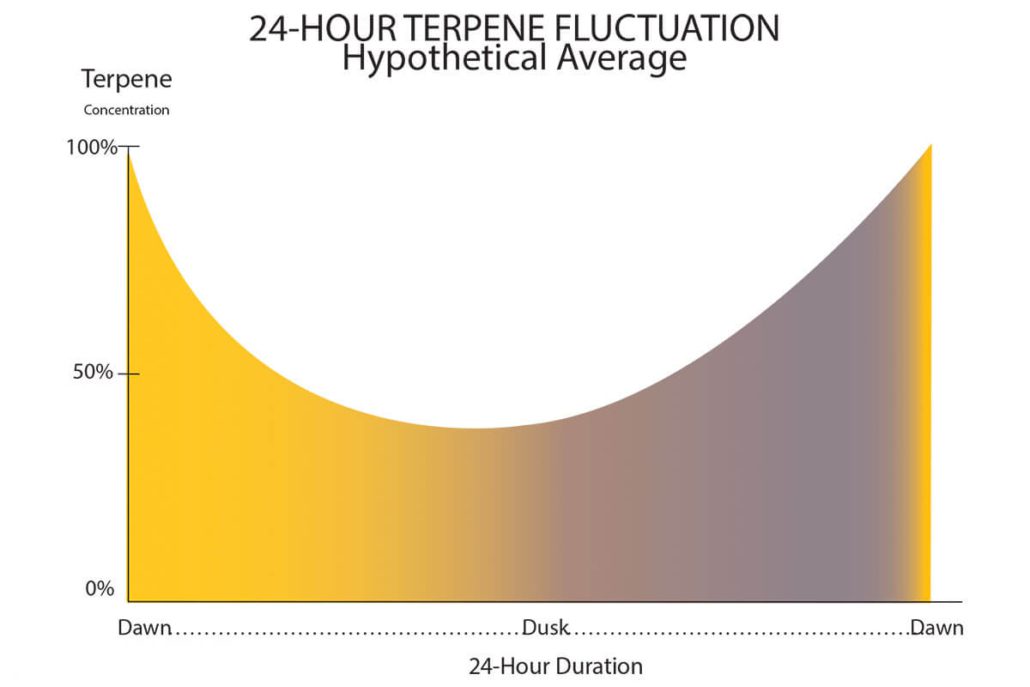
Image source: Ed Rosenthal
Terpene concentrations ascend during the nocturnal phase, peaking just before dawn, only to dissipate throughout the day, permeating the surroundings with their distinct aroma as a natural deterrent against potential threats. Come dusk, both terpene and cannabinoid levels ebb to their nadir.
The aromatic symphony we attribute to plants predominantly owes its existence to terpenes and flavonoids. While perceptible to our senses of smell and taste, these compounds wield influence beyond mere sensory perception. Terpenes, in particular, exert a nuanced impact on brain function, subtly altering the psychoactive effects of THC. This modulation extends to mood, sensitivity, and cognitive faculties, encompassing realms like balance and pain perception.
Certain terpenes exert their influence by binding to specific receptor sites in the brain, thereby modulating neurotransmitter release or altering membrane permeability, thereby regulating the influx of THC. Others intervene in neurotransmitter systems like serotonin and dopamine, modulating their activity and dynamics. This intricate interplay of terpenes orchestrates a diverse array of effects on mood, cognition, and bodily sensations.
The amalgamation of terpenes, as found in natural plant oils, engenders a complex interaction wherein each constituent contributes to the overall impact on brain function. Some combinations synergize, enhancing desired effects, while others may act antagonistically. Nevertheless, the unique composition of terpenes in each botanical blend crafts a distinctive “recipe” that shapes individual mood states and emotional experiences.
More Than A Hundred Terpenes Have Been Discovered In Cannabis.

Image source: surterra
More than a hundred distinct terpenes have been cataloged within the cannabis plant. Yet, this number belies the true diversity when considering the myriad variations of each terpene. Take, for example, the unmistakable citrus scent present in fruit rinds; while oranges and lemons emanate differing aromas, their terpenes, known as limonenes, exhibit near-mirror images of each other. These subtle discrepancies stem from variations in limonene quantities and other contributing compounds within citrus fruits.
Terpenes, synthesized within the trichomes of cannabis, share the same biosynthetic origin as THC. Comprising approximately 10-30% of marijuana smoke resin, these aromatic compounds exist in a complex array, with some terpenes sporadically appearing while others remain consistently present. The composition and proportions of terpenes vary widely among cannabis cultivars, manifesting in distinct olfactory profiles that discerning enthusiasts readily discern.
Interestingly, parallels between cannabis terpenes and those found in common herbs like black pepper have been noted by researchers, suggesting a broader botanical convergence in terpene production. This synthesis occurs within the trichomes, where THC production also takes place.
The cyclical rhythms of cannabis growth further influence terpene production, with plants typically harboring higher terpene levels following the dark period. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure play pivotal roles, with terpene concentrations fluctuating in response. Notably, terpenes evaporate readily under sunlight and elevated temperatures, resulting in diminished levels during peak daylight hours.
Moreover, environmental conditions, including climate, soil composition, and cultivation practices, profoundly impact terpene and flavonoid expression. Even within a single cannabis variety, variations in terpene profiles can arise, reflecting the intricacies of cultivation methods and environmental influences.
In essence, the captivating symphony of cannabis terpenes unfolds against a backdrop of dynamic environmental interactions, shaping the nuanced aromatic and therapeutic qualities cherished by cannabis aficionados worldwide.
Presented Below Are 10 Terpenes Typically Found In Abundance Within Cannabis.
Variations among individual plants are considerable, not only in the overall terpene content but also in the ratios of these aromatic compounds.
10. CINEOLE

Image source: royalqueenseeds
Cineole, the predominant compound found in eucalyptus oil, emits a distinctive camphor-minty fragrance reminiscent of pulegone. Beyond its association with eucalyptus, cineole is also encountered in various other aromatic plants. Moreover, while present in minor quantities, traces of cineole can be detected within marijuana, contributing subtly to its overall aroma and flavor profile.
9. PULEGONE
Image source: leafwell
Pulegone is characterized by its invigorating minty-camphor aroma and flavor, which are frequently utilized in the confectionery industry to impart a refreshing taste sensation. Despite its subtle presence, pulegone can be discerned in trace amounts within marijuana, contributing a nuanced layer of its unique essence to the overall olfactory and gustatory profile of the plant.
8. LINALOOL

Image source: hydroponique
Linalool emanates a delicate floral scent reminiscent of the blossoms of spring, particularly evoking the fragrant allure of lily of the valley, complemented by subtle spicy undertones. Derived from sources such as lavender, neroli, and various essential oils, this aromatic compound possesses a remarkable potency, with humans capable of detecting it in the air even at minute concentrations of one part per million (ppm). Noteworthy is linalool’s pivotal role as a primary component in numerous calming essential oils revered for their sedative effects, further underscoring its significance in aromatherapy and wellness practices.
7. DELTA-3-CARENE

Image source: botanyfarms
Delta-3-Carene exudes a tantalizingly sweet aroma with subtle pungency, evoking the resinous essence of pine and cedar. Widely distributed across various plant species, including rosemary, this terpene is recognized for its potential role in eliciting the sensation of dry eyes and mouth commonly associated with marijuana consumption.
6. BORNEOL

Image source: true-blue
Borneol exudes an aroma reminiscent of the menthol-like fragrance commonly associated with camphor, with the capacity to easily convert into this compound. Although found in modest quantities within various essential oils, borneol is frequently sourced commercially from plants such as artemisia, including wormwood, and certain cinnamon species.
The discernible camphor-like notes discerned in Silver Haze varieties serve as a distinct indicator of borneol’s inclusion, contributing to the characteristic olfactory profile unique to these strains.
5. TERPINEOL

Image source: greengoddesscollective
Terpineol emanates a fragrance reminiscent of lilac, citrus, or apple blossom infused with notes of lime. While it constitutes a minor fraction of numerous plant essential oils, it serves as a coveted ingredient in perfumery and soap-making for its aromatic properties.
Commercially sourced terpineol is often derived through the processing of other terpenes, further augmenting its versatility and applicability in various industries.
4. PINENE

Image source: 2fast4buds
Pinene evokes the recognizable scent of pine trees and their resinous compounds. While prominently present in various plant essential oils, including rosemary, sage, and eucalyptus, pinene contributes to their distinctive aromatic profiles.
It is probable that pinene plays a significant role in imparting the characteristic odor to certain cannabis varieties, particularly those bearing a resemblance to the pungent aroma of skunk.
3. B-CARYOPHYLLENE

B-Caryophyllene emerges as a prominent terpene present in various botanical sources such as black pepper (15-25%), clove (10-20%), and cotton (15-25%). Characterized by its sweet, woody aroma reminiscent of dry cloves, this terpene offers a palate of flavors ranging from peppery spiciness to hints of camphor and astringent citrus undertones. Its inclusion significantly contributes to the robust spiciness associated with black pepper and finds industrial application in enhancing tobacco flavor profiles.
Ingested in significant quantities, B-Caryophyllene acts by blocking calcium and potassium ion channels, thereby mitigating pressure exertion by heart muscles. Furthermore, when applied topically, it demonstrates analgesic properties, making it a preferred ingredient in clove oil, a well-known remedy for toothaches. Notably, B-Caryophyllene interacts with CB2 receptor sites, the same targets for cannabidiol, suggesting potential anti-inflammatory effects. Its subtle woody essence adds depth to the overall flavor profile.
2. LIMONENE

Image source: takomawellness
Abundant in the zest of citrus fruits and various other botanical sources, limonene ranks among the top terpenes found in cannabis resin, occupying the second, third, or fourth position depending on the strain. The unmistakable aroma of citrus rinds, released in a burst of fragrance upon peeling, owes its identity to the intricate structure of limonene.
Renowned for its multifaceted therapeutic properties, limonene exhibits potent antibacterial, antifungal, and anticancer activities. Its efficacy in combating fungal pathogens and potential carcinogens present in cannabis smoke streams underscores its significance in promoting respiratory health. Moreover, limonene acts synergistically to enhance the absorption of other terpenes by facilitating their penetration through cell membranes.
In humans, limonene demonstrates remarkable bioavailability, swiftly traversing the blood-brain barrier to elicit physiological responses. This includes an elevation in systolic blood pressure, indicative of heightened alertness and restlessness. Additionally, various analogs of limonene hold promise in modulating cognitive states, ranging from enhancing libido to fostering a sense of buoyancy or focused attention.
Notably, limonene-based sprays have emerged as a therapeutic intervention for depression, harnessing the terpene’s mood-lifting properties to alleviate symptoms and enhance emotional well-being.
1. MYRCENE

Image source: 2fast4buds
Among the plethora of terpenes found in cannabis, myrcene stands out as the most abundant across various strains. Beyond its prevalence in marijuana, myrcene is also notably present in significant quantities in hops, lemongrass, West Indian bay tree (utilized for bay rum production), verbena, and the plant from which it derives its name, myrcia. This versatile terpene is also detected in trace amounts within the essential oils of numerous other plant species.
Characterized by its complex aroma, myrcene exhibits notes reminiscent of cloves, earthiness, nuttiness, green vegetation, and citrus. These diverse scent profiles arise from subtle variations in the overall composition of essential oils. Indeed, these aromatic nuances are frequently employed to describe the distinctive fragrance of cannabis.
Interestingly, ripe mangoes are known to contain elevated levels of myrcene. Consuming a slightly overripe mango approximately 20 to 30 minutes prior to using marijuana allows myrcene to enter the bloodstream, potentially facilitating its interaction with THC. While the exact mechanism remains speculative, it is proposed that myrcene may aid THC in crossing the blood-brain barrier, thereby intensifying and hastening the onset of the psychoactive effects. This synergistic interaction between THC and myrcene is believed to culminate in a more potent and expeditious high.
In the same way that there is no universally agreed-upon favorite flavor of ice cream, there isn’t a single perfect combination of terpenes for everyone. Individual tastes, preferences, and circumstances all play a role in determining the ideal terpene profile for each person at any given time. However, by taking note of scents that are either favored or despised, individuals can better navigate toward cannabis strains that suit their specific preferences and needs.
As we unravel the complex interplay of terpenes within the cannabis plant, it becomes evident that these aromatic compounds are far more than mere fragrances—they are the architects of the enthralling sensory experience and the guardians of therapeutic potential. By understanding the distinct characteristics and effects of each terpene, cannabis enthusiasts and medical users alike can navigate the diverse landscape of strains with newfound appreciation and insight, unlocking the full spectrum of nature’s botanical treasures.

